42 Interior, Damong Maliit Rd, Novaliches, Quezon City, 1123 Metro Manila

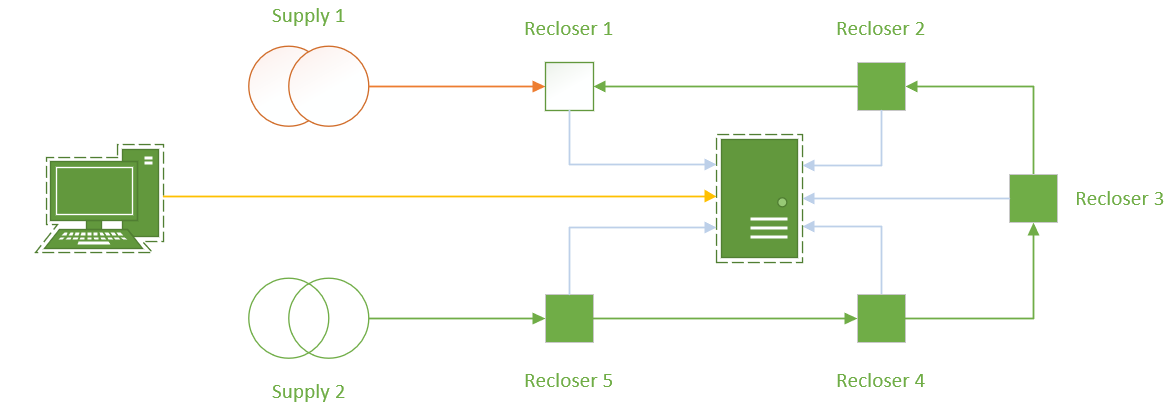
Figure 1 – Simplified Network Diagram of a Centralised Automation Scheme
In our previous edition, we explored the performance of centralised automation and the applicability of the IEC 61499 PLC standard for sharing of information. Whilst IEC 61499 provides a method for communication of device status between Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), the latency of performance lends its applicability to providing tailored data for centralised processing systems (such as in figure 1), rather than high performance peer to peer schemes.
GOOSE Messaging however is optimised for rapid distribution of messaging between IEDs. Distributed automation achieved at the IED asset site requires an extra close-onto-fault when communications are not present, but this can be resolved at high speed with using GOOSE messaging.
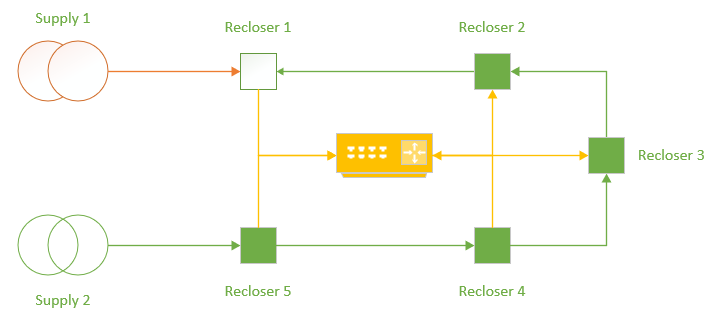
Figure 2 – Ring Mode Network with High Speed Communications Infrastructure for transporting GOOSE Messaging
If the centralised system is redesigned as high-speed communications LAN, IEC 61850 GOOSE messaging can be used to publish trip and block commands to other connected devices based on the performance.
For instance, if Recloser 2 were to see a downstream fault condition, it could trip and issue a GOOSE message asking Recloser 3 to block the automation condition.
A further improvement would be if Recloser 1 trips on a fault between Recloser 1 and Recloser 2, it could issue a GOOSE message to trip Recloser 2 prior to the close operation of Recloser 3, providing fault isolation prior to supply restoration, minimising fault reenergisation impacts and providing optimum network re-switching to restore supply.
NOJA Power’s OSM Recloser system has IEC 61850 communications capabilities as standard, and when coupled with high speed communications between devices it can be used for comprehensive automation schemes employing blocking and tripping messages to optimise the performance of DSA.